Chemical Properties
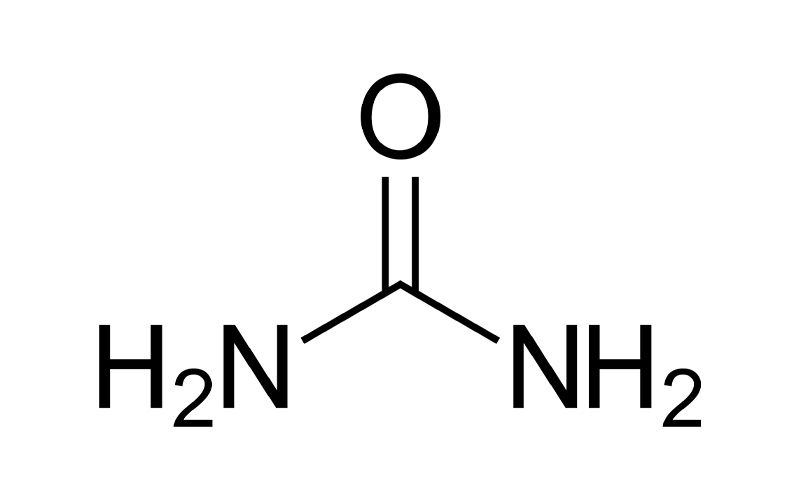
- Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH2)2. This amide has two amino groups (–NH2) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
- Urea can react with acid to form salts. It has hydrolysis. It can undergo condensation reaction at high temperature to form biuret, triuret and cyanuric acid.
- Urea can hydrolyze to form ammonia and carbon dioxide under the action of acid, alkali and enzyme (acid and alkali need to be heated).
- Urea is stable at room temperature and pressure. It is unstable to heat and will deaminate to form biuret when heated to 150~160℃. Copper sulfate and biuret react to form purple color, which can be used to identify urea [3]. If heated rapidly, it will deaminate and trimerize to form the six-membered ring compound cyanuric acid. (Mechanism: first deaminate to form isocyanic acid (HN=C=O), then trimerize.)
- It can react with acetyl chloride or acetic anhydride to form acetylurea and diacetyl urea.
- It reacts with diethyl malonate under the action of sodium ethoxide to form malonyl urea (also known as barbituric acid, because it has a certain acidity).
- 00:58
- Urea-formaldehyde resin: Resin produced by the reaction of urea and formaldehyde
- Under the action of alkaline catalysts such as ammonia water, it can react with formaldehyde and condense into urea-formaldehyde resin.
Uses
- Agriculture: More than 90% of world industrial production of urea is destined for use as a nitrogen-release fertilizer.
- Resins: Urea is a raw material for the manufacture of formaldehyde based resins, such as UF, MUF, and MUPF, used mainly in wood-based panels, for instance, particleboard, fiberboard, OSB, and plywood.
- Explosives: Urea can be used in a reaction with nitric acid to make urea nitrate, a high explosive that is used industrially and as part of some improvised explosive devices.
- Automobile systems: Urea is used in Selective Non-Catalytic Reduction (SNCR) and Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) reactions to reduce the NOx pollutants in exhaust gases from combustion from diesel, dual fuel, and lean-burn natural gas engines.
- Many other uses.
Preparation method
Calcium cyanamide method
Urea is industrially produced using calcium cyanamide as raw material. Under the action of sulfuric acid, calcium cyanamide generates cyanamide, which then reacts with water to generate urea. The reaction equation is as follows
However, it has not been applied on a large scale industrially due to the difficulty in obtaining raw materials, toxicity, difficulty in controlling reaction conditions, and unreasonable economy.
CO2 method
In 1922, the German Farben Oppau plant built the world’s first industrial device for producing urea using ammonia and carbon dioxide as raw materials, which is the basis of modern urea production technology. In industry, urea is prepared under high temperature and high pressure using carbon dioxide and liquid ammonia as raw materials. Its chemical equation is as follows
Due to the advantages of easy availability of raw materials, high atomic utilization rate, high product concentration, controllable reaction conditions and simple process flow, this method is currently widely used in the world to directly prepare urea using ammonia and carbon dioxide.
The process for preparing urea using carbon dioxide as raw material can be divided into aqueous solution full circulation method, carbon dioxide stripping method and ammonia stripping method. The cost of the aqueous solution full circulation method is relatively high. The carbon dioxide stripping method has fewer equipment, simpler processes, and lower energy consumption than the former. Compared with the ammonia stripping method, it has the advantages of lower stripping pressure and higher stripping efficiency. Therefore, in recent years, most new urea plants and large-scale urea plant renovations have adopted this process.
Properties
| Chemical formula | CO(NH2)2 |
| Molar mass | 60.06 g/mol |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.32 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 133 to 135 °C (271 to 275 °F; 406 to 408 K) |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
| Solubility in water | 545 g/L (at 25 °C) |
| Solubility | 500 g/L glycerol 50 g/L ethanol ~4 g/L acetonitrile |
| Basicity (pKb) | 13.9 |
| Conjugate acid | Uronium |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −33.4·10−6 cm3/mol |
Our company specializes in hazardous chemicals, flammable and explosive chemicals, toxic chemicals (legal export), ultra-pure and high-purity reagents. Welcome to contact us.
Packing and shipping