nitric acid Ultrapure Reagent CAS 7697-37-2
| English Name | Nitric acid |
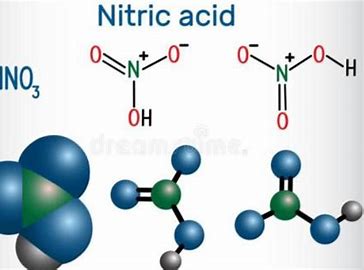
| Chemical Formula | HNO₃ |
| Molecular Weight | 63.01 g/mol |
| CAS Number | 7697-37-2 |
| EINECS Number | 231-714-2 |
| Appearance | Pure nitric acid is a colorless transparent liquid. Concentrated nitric acid is pale yellow. |
| Odor | Pungent and suffocating |
| Density | 1.41 g/mL at 20°C (68% solution) |
| Melting Point | -42°C (anhydrous) |
| Boiling Point | 120.5°C (68% solution) |
| Solubility in Water | Miscible |
| Acidity (pH) | 1.08 (100 mM solution) |
| Storage Conditions | Store at +2°C to +25°C |
| Sensitivity | Hygroscopic |
| Color | Colorless to deep yellow |
| Flash Point | 120.5°C |
| Vapor Pressure | 8 mm Hg at 20°C |
| Vapor Density | 1 (vs air) |
These specifications are for Nitric Acid intended for demanding applications in laboratories, research, and manufacturing where trace impurity levels are critical.
| Parameter | Specification | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Nitric Acid (HNO₃) (w/w) | 67 – 70 | % |
| Trace Impurities | ||
| Aluminum (Al) | ≤ 20 | ppt |
| Antimony (Sb) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Arsenic (As) | ≤ 20 | ppt |
| Barium (Ba) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Beryllium (Be) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Bismuth (Bi) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Boron (B) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Cadmium (Cd) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Calcium (Ca) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Cerium (Ce) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Cesium (Cs) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Chromium (Cr) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Cobalt (Co) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Copper (Cu) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Dysprosium (Dy) | ≤ 1 | ppt |
| Erbium (Er) | ≤ 1 | ppt |
| Europium (Eu) | ≤ 1 | ppt |
| Gadolinium (Gd) | ≤ 1 | ppt |
| Gallium (Ga) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Germanium (Ge) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Gold (Au) | ≤ 20 | ppt |
| Hafnium (Hf) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Holmium (Ho) | ≤ 1 | ppt |
| Indium (In) | ≤ 1 | ppt |
| Iron (Fe) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Lanthanum (La) | ≤ 1 | ppt |
| Lead (Pb) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Lithium (Li) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Lutetium (Lu) | ≤ 1 | ppt |
| Magnesium (Mg) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Mercury (Hg) | ≤ 50 | ppt |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Neodymium (Nd) | ≤ 1 | ppt |
| Nickel (Ni) | ≤ 20 | ppt |
| Niobium (Nb) | ≤ 1 | ppt |
| Palladium (Pd) | ≤ 20 | ppt |
| Platinum (Pt) | ≤ 20 | ppt |
| Potassium (K) | ≤ 10 | ppt |
| Praseodymium (Pr) | ≤ 1 | ppt |
Nitric acid (HNO3) is a fundamental inorganic acid, crucial across various industries due to its potent corrosive and oxidizing properties. At Yuhan Chemical, we provide top-tier nitric acid, known for its purity and reliability.
Our nitric acid is typically colorless. It boils at 78.2°C and solidifies when fully cooled.
Yuhan Chemical’s nitric acid is extensively used in sectors globally.
It’s a cornerstone for producing fertilizers like ammonium nitrate.a vital raw material for explosives such as nitroglycerin and TNT.
Beyond these, our nitric acid is indispensable in manufacturing dyes. for metallurgical processes like ore flotation and steel etching.
in photographic engraving, and for reprocessing spent nuclear fuel.
We primarily produce our nitric acid via the efficient Ostwald process. While other methods exist, Yuhan Chemical focuses on delivering industrial-grade pure nitric acid that meets your most stringent production standards. Choose Yuhan Chemical’s nitric acid for reliable, efficient, and safe performance.
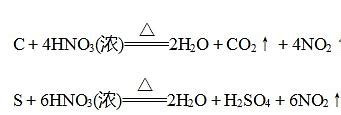
Applications of Nitric Acid
| Application Category | Specific Use Cases & Details | Chemical Formulas / Formulas / Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Production | Fertilizers: Used to produce ammonium nitrate, a vital component for agricultural fertilizers. | NH_3+HNO_3rightarrowNH_4NO_3 |
| Plastics & Dyes: Essential in the manufacturing process of various plastics and synthetic dyes. | (General organic synthesis, often involving nitration or oxidation reactions) | |
| Explosives: Key raw material for powerful explosives like nitroglycerin and trinitrotoluene (TNT). | Nitroglycerin: Formed by nitration of glycerol. <br> TNT: Formed by successive nitration of toluene. | |
| Metallurgy & Refining | Aqua Regia Formation: When combined with hydrochloric acid (HCl), it forms aqua regia (Latin for “royal water”), a highly corrosive mixture capable of dissolving noble metals like gold and platinum. | HNO_3(aq)+3HCl(aq)rightarrowNOCl(g)+Cl_2(g)+2H_2O(l) <br> (This initial reaction generates nitrosyl chloride and chlorine gas, which then react with the noble metals.) |
| Ore Flotation & Etching: Used in the process of ore flotation and for etching steel. | (Specific reactions vary depending on the ore and metal, generally involving oxidation of metal surfaces.) | |
| Photographic Engraving: Employed in the creation of photographic engravings. | (Involves etching metal plates for printing.) | |
| Analytical & Laboratory Testing | Chloride Testing (Schools): Used in school science labs to test for chlorides. Nitric acid acidifies the sample, and then silver nitrate (AgNO_3) is added. If chloride ions (Cl−) are present, a white precipitate of silver chloride (AgCl) forms. | AgNO_3(aq)+Cl−(aq)rightarrowAgCl(s)downarrow+NO_3−(aq) <br> (The nitric acid prevents other ions from precipitating with silver.) |
| Colorimetric Tests: Used in qualitative tests to differentiate between certain alkaloids, e.g., heroin and morphine, by producing distinct color changes. | (Specific color reactions occur due to oxidation or other chemical changes induced by nitric acid on the alkaloid’s structure.) | |
| Sample Digestion for Elemental Analysis: Commonly used to digest turbid water samples, solid sludge, and other complex samples before elemental analysis via techniques like ICP-MS, ICP-OES, ICP-AES, GFAA, and flame atomic absorption spectrometry. | (Strong oxidative power breaks down organic matrices, releasing metal ions for analysis.) | |
| Medical & Pharmaceutical | Caustic Agent: In its pure state, it’s used as a caustic substance to remove chancres and warts in the medical field. | (Corrosive action on biological tissue.) |
| Indigestion Treatment: Diluted solutions are used to treat indigestion. | (Acts as an acidic digestive aid in very dilute forms, though less common now.) | |
| Aerospace & Propulsion | Rocket Oxidizer: Used in various forms as an oxidizer in liquid fuel rockets. | Forms include: <br> – Red Fuming Nitric Acid (RFNA): HNO_3 with dissolved nitrogen dioxide (NO_2). <br> – White Fuming Nitric Acid (WFNA): Nearly pure HNO_3. <br> – Mixtures with sulfuric acid or with HF inhibitors (e.g., Inhibited Red Fuming Nitric Acid, IRFNA). |
| Organic Synthesis | Nitration: Used to introduce nitro groups (−NO_2) into organic molecules, particularly aromatic compounds like benzene. When used with sulfuric acid (H_2SO_4), it forms the highly reactive nitronium ion (NO_2+), which acts as an electrophile in aromatic substitution. | HNO_3+2H_2SO_4rightleftharpoonsNO_2++2HSO_4−+H_3O+ <br> Benzene Nitration: <br> C_6H_6+HNO_3xrightarrowH_2SO_4C_6H_5NO_2+H_2O |
| Electrochemistry | Chemical Dopant: Used as a chemical dopant for organic semiconductors to modify their electrical properties. | (Introduces electron-withdrawing nitro groups or oxidizes the semiconductor, altering its conductivity.) |
| Carbon Nanotube Purification: Essential in the purification process of carbon nanotube feedstock, removing impurities and functionalizing the nanotubes. | (Oxidizes and dissolves amorphous carbon and metallic catalyst impurities, often creating carboxylic acid groups on the nanotube surface.) | |
| Woodworking | Artificial Wood Aging: At low concentrations, it’s used to artificially age pine and maple wood, imparting a gray-gold color similar to very old wax- or oil-finished wood. | (Reacts with lignin and cellulose in the wood, causing oxidation and darkening, simulating decades of natural aging.) |
| Forensics / Drug Testing | Alkaloid Spot Check: Can be used as a spot test reagent for alkaloids like LSD, producing a variety of colors depending on the specific alkaloid present. | (Specific color reactions occur due to complex chemical interactions, often involving oxidation, with the alkaloid’s unique structure.) |
Nitric Acid 65% (Ultrapure): Safety & Handling Essentials
Nitric Acid, Its exceptional purity makes it highly effective, but its inherent properties demand the utmost respect and strict adherence to safety protocols. At [Your Company Name, if applicable, otherwise remove], we prioritize the safe use and handling of Nitric Acid. Understanding its hazards and proper precautions is paramount for anyone working with this powerful substance.

Understanding the Hazards of Ultrapure Nitric Acid 65%
When working with Nitric Acid 65% (Ultrapure), recognizing its potential dangers is the first step toward safe handling. The following classifications and statements, typically found on its Safety Data Sheet (SDS), highlight these critical hazards:
- Signal Word: DANGER This alerts users to the most severe hazards associated with the chemical.
- Hazard Categories:
- Acute Toxicity Category 3: Indicates that the substance can be toxic if inhaled. Even short exposure to concentrated fumes can be harmful or fatal.
- Corrosive to Metals Category 1: Nitric Acid aggressively reacts with and degrades many metals, releasing hydrogen gas which can be flammable.
- Oxidizing Liquid Category 3: This means Nitric Acid can intensify a fire or cause combustible materials to ignite. It provides oxygen to a fire, making it harder to extinguish.
- Skin Corrosion/Irritation Category 1A: This is the most severe classification for skin contact, meaning it causes irreversible damage to skin, including severe burns.
Critical Hazard Statements (H-Statements)
These statements provide specific details about the nature of the chemical’s hazards:
- H272 – May intensify fire; oxidizer. This emphasizes its role in escalating fires, providing oxygen to fuel the flames.
- H290 – May be corrosive to metals. A warning about its destructive effect on metallic surfaces.
- H314 – Causes severe skin burns and eye damage. Highlights the extreme danger of direct contact with skin and eyes, leading to severe chemical burns.
- H331 – Toxic if inhaled. A crucial alert regarding the dangers of inhaling its vapors or mists, which can cause respiratory distress or worse.
- EUH071 – Corrosive to the respiratory tract. This specific EU (European Union) hazard statement reinforces that even its fumes are highly corrosive to the lungs and airways.
Essential Precautionary Measures (P-Statements)
Given the significant hazards of Nitric Acid 65% (Ultrapure), strict precautionary measures are not optional – they are mandatory. Adhering to these guidelines protects personnel and ensures operational safety.
- P260 – Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray. This is paramount. Always ensure adequate ventilation, preferably in a fume hood, to prevent inhalation of hazardous fumes.
- P280 – Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. Comprehensive Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is non-negotiable. Chemical-resistant gloves (e.g., neoprene, PVC), full-body chemical suits or aprons, safety goggles, and a face shield are essential to prevent direct contact.
- P301+P330+P331 – IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. Immediate action for ingestion. Rinsing the mouth helps clear residual acid, but inducing vomiting can cause further damage to the esophagus. Seek immediate medical attention.
- P305+P351+P338 – IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continue rinsing. Eye exposure requires immediate and prolonged flushing with water. Access to an eyewash station is critical.
- P308+P313 – IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. In case of any exposure or if health concerns arise after handling, professional medical evaluation is crucial.
Safe Storage and Handling Practices
Beyond the immediate precautionary statements, safe handling of Nitric Acid involves proper storage and robust emergency preparedness:
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from incompatible materials (e.g., organic compounds, reducing agents, flammable materials, strong bases, and most metals). Use corrosion-resistant containers (e.g., glass, certain plastics).
- Ventilation: Always work in a well-ventilated area or under a certified fume hood to control airborne concentrations.
- Dilution: When diluting Nitric Acid, always add acid slowly to water, never water to acid, to manage the exothermic reaction and prevent splashing.
- Emergency Preparedness: Have spill kits, emergency showers, and eyewash stations readily accessible in all areas where Nitric Acid is handled.
Partnering for Safety with High-Purity Nitric Acid
At [Your Company Name, if applicable, otherwise remove], we are committed to providing ultrapure Nitric Acid that meets the highest industry standards, coupled with comprehensive safety information. Understanding and rigorously applying these safety guidelines is not just a recommendation; it’s a fundamental requirement for the responsible use of Nitric Acid 65% (Ultrapure).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Why is Nitric Acid 65% considered an oxidizer? It’s an oxidizer because it readily provides oxygen to other substances, which can intensify a fire or cause combustible materials to ignite.
- What PPE is absolutely essential when handling Nitric Acid? Essential PPE includes chemical-resistant gloves, eye protection (goggles and face shield), and chemical-resistant clothing/apron.
- What should I do if Nitric Acid splashes on my skin? Immediately rinse the affected area with copious amounts of water for at least 15-20 minutes. Remove contaminated clothing. Seek immediate medical attention.
- Can Nitric Acid be stored near other chemicals? No. Nitric Acid must be stored separately from incompatible materials such as organic compounds, reducing agents, flammable liquids, strong bases, and most metals to prevent dangerous reactions.
- Where can I find more detailed safety information for Nitric Acid? Always consult the product’s full Safety Data Sheet (SDS) provided by the supplier. This document contains comprehensive information on hazards, handling, storage, first aid, and emergency procedures.