Sodium Citrate: A “Miracle” Ingredient with Versatility and Safety
What is Sodium Citrate?
In modern life, many products we encounter daily hide some “behind-the-scenes heroes,” and sodium citrate is one of them.
| Item | Information |
|---|---|
| English Name | Sodium Citrate |
| CAS Number | 68-04-2 (anhydrous); 6132-04-3 (dihydrate) |
| Molecular Formula | C₆H₅Na₃O₇ (anhydrous); C₆H₅Na₃O₇·2H₂O (dihydrate) |
| Molecular Weight | 258.07 (anhydrous); 294.10 (dihydrate) |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals or white crystalline powder |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Cool and salty taste |
| Solubility | Soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol |
| Melting Point | >300°C (anhydrous); loses water of crystallization at 150°C (dihydrate) |
| Boiling Point | 309.6°C at 760 mmHg |
| pH of Aqueous Solution | 5% aqueous solution: pH 7.6–8.6; 10% aqueous solution: pH 3.4–3.8 |
| Stability | Stable in air and at room temperature |
| Preparation Method | Prepared by neutralization of citric acid with sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate, followed by concentration and crystallization |
| Uses | Used as a pH regulator, emulsifier, and stabilizer in the food industry; as an anticoagulant in medicine; and as a cleaning agent in industry |
The “Chemical ID Card” of Sodium Citrate
To truly understand sodium citrate, let’s first look at its “chemical ID card”:
CAS Number of Sodium Citrate:
In chemical registration, sodium citrate has its unique identifiers: its CAS numbers are typically 68-04-2 (anhydrous) or 6132-04-3 (dihydrate).
Applications in the Medical Field:
Sodium citrate plays an important role in the medical field:
- Blood Anticoagulant:used anticoagulants during blood collection and storage. Sodium citrate binds with calcium ions in the blood, preventing blood coagulation and ensuring the integrity of blood samples.
- Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections: It can act as a urine alkalinizer. It relieves symptoms caused by urinary tract infections by changing the urine’s pH, which inhibits bacterial growth.
- Other Medical Uses: Sodium citrate is also used in some oral rehydration salts help the body replenish electrolytes.
Applications in the Food Industry:
Are you curious why some foods stay fresh and delicious? This often involves sodium citrate. As an important food additive, sodium citrate’s application in food is very extensive:
- Dairy Products: In cheese, condensed milk, and ice cream, sodium citrate acts as an emulsifier and stabilizer, preventing fat separation and making the product’s texture smoother and more uniform.
- Beverages: It can serve as an acidity regulator, balancing the sweet and sour taste of beverages, while also enhancing the flavor of some fruits.
- Meat Products: In processed meat products, sodium citrate can act as a preservative, delaying fat oxidation, and as an emulsifying salt to help the meat become firmer.
- Baked Goods: In some baked products, it can improve dough structure, making the finished product softer.
Applications in Other Industries:
Besides medicine and food, sodium citrate also plays a role in other industrial fields:
- Cleaning Agents: It can act as a water softener, reducing calcium and magnesium ions in water and improving washing efficiency.
- Cosmetics: In certain cosmetics, sodium citrate is used as a pH adjuster and preservative.
Safety Assessment of Sodium Citrate
Is Sodium Citrate Safe for Humans?
Many people are probably concerned: Is sodium citrate safe for humans? The answer is: yes, sodium citrate is safe under normal use dosages. International authoritative organizations such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) have listed it as a safe substance. In food, it is widely considered “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS).
Of course, excessive intake of any substance can have an impact. In very rare cases, excessive intake of sodium citrate might lead to mild gastrointestinal discomfort.
Precautions for Consuming Sodium Citrate:
For most people, sodium citrate ingested through food is safe. However, individuals with specific health conditions, as their sodium intake may be restricted.
Distinction Between Sodium Citrate and “Salt”
Is Sodium Citrate Just Salt?
Some might ask, is sodium citrate just salt?
However, it’s not what we commonly refer to as “table salt”—sodium chloride. While both are salts, their chemical structures and mechanisms of action in the body are completely different. Sodium chloride primarily provides sodium and chloride ions, while sodium citrate provides citrate ions and sodium ions. Their functions in food and their metabolic pathways in the body differ significantly.
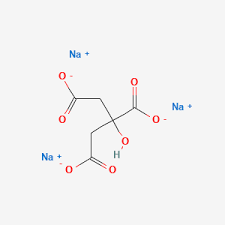
Sodium Citrate: Guardian of Food and Health
In conclusion, sodium citrate is a versatile and safe compound. It plays an important role in the food industry, helping us enjoy more delicious and stable products; in the medical field, it provides crucial support for disease treatment and blood preservation; and in other industries, it also silently contributes its strength. It is precisely because of the existence of sodium citrate that our modern lives have become more convenient and colorful.