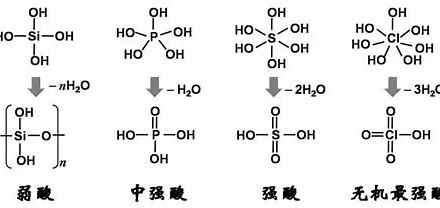
Tripotassium Phosphate (TKP)Cleaning /human hazards
I. What is Tripotassium Phosphate?
Have you ever wondered about the ingredients lurking in your favorite processed foods or household cleaning products? One such ubiquitous compound, often overlooked, is Tripotassium Phosphate, commonly abbreviated as TKP.

| Item | Information |
|---|---|
| IUPAC Name | Potassium phosphate/Tripotassium Phosphate/TKP |
| Molecular Formula | K3PO4 |
| CAS Number | 7778-53-2 |
| Synonyms | Tripotassium phosphate, Potassium orthophosphate, Potassium tertiary phosphate, Tripotassium monophosphate, Potassium phosphate tribasic |
| InChI | InChI=1S/3K.H3O4P/c;;;1-5(2,3)4/h;;;(H3,1,2,3,4)/q3*+1;/p-3 |
| Molecular Weight | 212.27 g/mol |
| Physical Appearance | Colorless or white crystalline solid |
| Density | 2.564 g/cm³ at 17°C |
| Melting Point | 1,380°C |
| Solubility in Water | Very soluble, 90 g/100mL at 20°C |
| pH | Strongly alkaline |
| Application | Buffering agent, catalyst, food additive, fertilizer, etc. |
| Safety Information | Irritant to skin, eyes, and respiratory system |
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of TKP, addressing critical questions about its safety, diverse applications, and what it actually does to your body.
II. The Many Uses of Tripotassium Phosphate: A Versatile Compound
Tripotassium Phosphate (TKP) is a true workhorse, finding applications in both the food industry and various industrial sectors.

A. Applications in the Food Industry:
In the realm of food, TKP is a widely approved food additive, often designated as E340(iii) in Europe. Its functions are crucial for the quality and longevity of many products:
- Acidity Regulator (Buffering Agent): TKP helps maintain a stable pH level in food products, preventing undesirable changes in taste and texture.
- Stabilizer and Emulsifier: It prevents ingredients from separating, ensuring a consistent texture in products like dairy alternatives and processed cheeses.
- Texturizer: In baked goods, TKP can improve dough consistency and crumb structure. In meats and seafood, it helps retain moisture, enhancing juiciness and tenderness.
- Nutrient Enhancer: As a source of essential minerals, TKP contributes both phosphorus and potassium to fortified foods.
You’ll commonly find Tripotassium Phosphate in:
- Processed foods (e.g., cereals, cheese spreads, baked goods)
- Sports drinks and nutritional supplements
- Meat and poultry products (as a curing agent)
- Dairy products and alternatives
B. Industrial and Laboratory Applications:
Beyond your dinner plate, TKP plays a significant role in various industrial processes:
- Cleaners and Degreasers: Its strong alkaline nature makes it an effective ingredient in heavy-duty cleaning products, stripping away grease and grime.
- Fertilizers: As a readily available source of potassium and phosphorus, TKP is used in agricultural fertilizers to promote healthy plant growth.
- Water Treatment Agents: TKP acts as a corrosion inhibitor, helps control scale buildup, and can adjust pH levels in water treatment systems.
- Alkaline Reagent in Organic Chemistry: In laboratory settings, TKP is utilized as a basic reagent for various chemical reactions.
- Other Industrial Uses: It also finds applications in the production of ceramics and in certain metal treatment processes.
1. Cleaners and Degreasers
- Examples:
- Industrial Cleaners: TKP is widely incorporated into heavy-duty industrial cleaning formulas, used for tackling grease and baked-on residues in factory workshops, on machinery, and in commercial kitchens.
- Degreasing in Water Treatment: In some industrial water treatment systems, TKP can serve as a pre-treatment agent, helping to remove oils, greases, and suspended solids from water to protect downstream equipment.
- Consequences/Implications as an Ingredient:
- Effective Cleaning: TKP is a strong alkaline substance. Its high pH effectively saponifies fats and oils (breaking them down into water-soluble soaps) and helps to disperse dirt, making it easier to rinse away.
- Emulsifying Action: It helps to emulsify water-insoluble oils and fats, keeping them stably suspended in water and preventing redeposition.
- Water Softening: The phosphate in TKP can bind with hard water ions like calcium and magnesium, softening the water and thereby increasing the efficiency of cleaning agents and reducing scale formation.
- Potential Corrosiveness: Due to its strong alkalinity, high concentrations of TKP solutions can be corrosive to certain metals (like aluminum) and sensitive surfaces.
- Environmental Impact: If discharged into the environment without proper treatment, phosphates can lead to eutrophication of water bodies, promoting excessive algae growth. This depletes oxygen in the water, negatively impacting aquatic ecosystems. Consequently, many regions have strict regulations on the use of phosphate-containing cleaners.
2. Fertilizers
- Examples:
- Liquid Fertilizers: TKP can be a component of highly concentrated liquid fertilizers, applied directly to the soil or via foliar sprays, providing plants with readily available phosphorus and potassium.
- Water-Soluble Fertilizers: In greenhouse cultivation or hydroponic systems, TKP is a common water-soluble fertilizer raw material due to its rapid dissolution and absorption by plants.
- Consequences/Implications as an Ingredient:
- Provides Essential Nutrients: Phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) are two of the main macronutrients required for plant growth.
- Promotes Growth: As a source of phosphorus and potassium, TKP can significantly promote healthy plant growth, increase yields, and improve crop quality.
- High Solubility: TKP’s high solubility means that plants can quickly and efficiently absorb its nutrients.
- Soil pH Impact: Its alkaline nature might have a slight effect on soil pH, which might require adjustment in certain cases.
- Risk of Over-Fertilization: Like all fertilizers, excessive use of TKP can lead to salt buildup in the soil and even “burn” plants, as well as increase the risk of phosphate runoff into water bodies, contributing to eutrophication.
3. Water Treatment Agents
- Examples:
- Boiler Water Treatment: In industrial boilers and cooling towers, TKP is used as a corrosion inhibitor and scale control agent. It prevents the buildup of mineral scale from calcium and magnesium and forms a protective layer to reduce metal corrosion.
- pH Adjustment: In industrial water circulation systems that require maintaining a specific pH range, TKP can serve as an effective pH adjusting agent.
- Consequences/Implications as an Ingredient:
- Prevents Equipment Damage: By inhibiting corrosion and scale formation, TKP extends the lifespan of industrial equipment, reduces maintenance costs, and improves system efficiency.
- Optimizes Water Quality: Stabilizing water body pH is critical for many industrial processes, and TKP helps achieve this.
- Phosphate Residue: The use of TKP in water treatment systems will result in phosphate residues, which need to be treated before discharge to prevent environmental pollution.
4. Alkaline Reagent in Organic Chemistry
- Examples:
- Phase Transfer Catalysis: In laboratory organic synthesis, TKP can act as a mild and effective base to facilitate specific reactions, such as deprotonation reactions of certain alcohols or phenols.
- Michael Addition Reactions: In some Michael addition or Knoevenagel condensation reactions, TKP can serve as a catalyst or additive to enhance reaction conversion and selectivity.
- Consequences/Implications as an Ingredient:
- Reaction Control: As an alkaline reagent, TKP can precisely control the acidity-alkalinity of the reaction environment, thereby directing the reaction towards the desired outcome and improving the yield of the target product.
- Enhanced Selectivity: In certain cases, using TKP as a base can improve the chemoselectivity of a reaction, reducing the formation of by-products.
- Optimization of Reaction Conditions: Its solubility and basicity make it a useful tool for optimizing specific organic synthesis reaction conditions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to some more expensive or hazardous organic bases, TKP can be a more economical and safer alternative, especially for laboratory-scale synthesis.
III. Tripotassium Phosphate and Your Body: Safety and Potential Risks
Given its widespread presence, understanding how Tripotassium Phosphate interacts with your body is paramount.
A. The Role of Phosphorus and Potassium in Your Body:
Both phosphorus and potassium are essential minerals vital for numerous bodily functions.
- Phosphorus: Plays a critical role in bone and teeth formation, energy production (as part of ATP), and DNA/RNA synthesis. Phosphate is crucial for cell growth and tissue repair. It’s also used to treat hypophosphatemia (low phosphate levels).
- Potassium: Essential for maintaining fluid balance, nerve signals, muscle contractions, and heart rhythm.
B. Safety and Regulation of Tripotassium Phosphate:
Generally, Tripotassium Phosphate is considered safe when consumed as a food additive within regulated limits by authorities like the FDA.
Important Considerations: Recent recommendations from organizations like the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) highlight the importance of overall phosphate intake. While TKP itself might be safe, excessive consumption from various sources (processed foods, supplements) could lead to elevated phosphate levels, particularly for children, adolescents, and individuals regularly taking phosphate-containing supplements. Moderation and dosage are key.
C. Potential Side Effects of Tripotassium Phosphate (High Doses or Sensitive Individuals):
While generally safe in typical food amounts, high doses or individual sensitivities can lead to:
- Gastrointestinal Discomfort: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Signs may include confusion, severe weakness, dizziness, irregular heartbeat, numbness, or tingling sensations.
- Kidney Function Issues: High phosphate levels (hyperphosphatemia) can be particularly problematic for individuals with pre-existing kidney disease.
- Skin and Eye Irritation: In non-food grade applications or accidental exposure, TKP can cause irritation.
- Respiratory Irritation: Inhalation of TKP dust can lead to respiratory discomfort.
D. Who Should Avoid or Be Cautious with Tripotassium Phosphate?
Certain individuals should exercise caution or avoid TKP:
- Those with pre-existing conditions like hyperkalemia (high potassium), hypocalcemia (low calcium), or hyperphosphatemia.
- Individuals with heart disease, kidney disease, or Addison’s disease.
Always consult your doctor or a healthcare professional if you have concerns.
| Condition | Risks and Effects | Specific Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Hyperphosphatemia | Disrupts calcium-phosphorus balance, causing calcium loss from bones and soft tissue calcification in blood vessels, kidneys, heart, and eyes. | Patients with kidney disease are at highest risk. Excess phosphate intake in such patients can lead to renal osteodystrophy (fragile bones, easy fractures) and vascular calcification, increasing cardiovascular disease risk and mortality. High phosphorus levels also promote calcium deposition in blood vessel walls, hardening them and increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke. Excessive phosphorus inhibits calcium absorption and causes calcium extraction from bones to balance blood phosphorus levels, leading to brittle bones and increased risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Chronic hyperphosphatemia can cause persistent skin itching, sometimes with rashes or hard nodules due to calcium deposits under the skin. |
| Hyperkalemia | Potassium in potassium phosphate can lead to high blood potassium levels, especially in those with kidney dysfunction or sensitivity to potassium. | Irregular heartbeats, bradycardia, and even cardiac arrest can occur due to interference with the heart’s electrical activity. High potassium affects neuromuscular function, causing muscle weakness, numbness, and potentially flaccid paralysis. Gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort may also appear. |
| Gastrointestinal Discomfort | Even with normal kidney function, large doses of potassium phosphate can cause digestive reactions. | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps may occur due to the direct irritation of the digestive tract by phosphates. |
| Specific Populations at Risk | Certain groups are more sensitive to potassium phosphate or unable to metabolize it safely due to underlying conditions. | Patients with kidney disease should strictly limit phosphate intake. Heart disease patients, especially those at risk of arrhythmias or heart failure, may have increased cardiac burden or adverse events from excess potassium and phosphorus. Patients with Addison’s disease have impaired potassium excretion due to insufficient cortisol and aldosterone secretion, leading to potassium accumulation. People taking ACE inhibitors or potassium-sparing diuretics, which already raise blood potassium levels, are at risk of severe hyperkalemia if they also consume potassium phosphate. High potassium levels increase the risk of digoxin toxicity. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should use potassium phosphate cautiously, as the potential effects on fetuses or infants need further research. |
IV. Common Misconceptions and Clarifications about Tripotassium Phosphate
A. Tripotassium Phosphate vs. Trisodium Phosphate (TSP):
It’s common to confuse Tripotassium Phosphate with Trisodium Phosphate (TSP). While both are phosphate salts and can have overlapping uses, they are distinct compounds. TSP is more widely recognized as a heavy-duty cleaner and degreaser in industrial settings, though some food-grade TSP exists. The primary concern about “cleaning agents in food” often stems from a misunderstanding of dosage and food-grade purity, which are strictly regulated for food additives.
B. Tripotassium Phosphate in Cheerios Cereal:
The presence of Tripotassium Phosphate in popular cereals like Cheerios has sometimes sparked consumer curiosity. It’s included in such products to regulate acidity and improve texture, contributing to the overall quality and shelf-stability of the cereal. Its inclusion is approved as a food additive, and its levels are carefully controlled to ensure safety for consumption.