Hydrogen Peroxide/7722-84-1/H2O2
Introduction to Hydrogen Peroxide
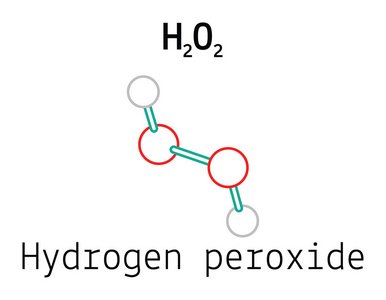
Hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) is a crucial chemical substance, which is widely used in the fields of medical treatment, chemical industry, and cleaning and disinfection in daily life. It is composed of two hydrogen atoms (H) and two oxygen atoms (O), and the oxygen atoms in the molecule are connected by a peroxide bond (O-O). This unique structure endows hydrogen peroxide with strong oxidizing properties. Hydrogen peroxide is a weakly acidic substance, and its acidity is slightly stronger than that of water. Under normal temperature conditions, hydrogen peroxide appears as a colorless and transparent liquid, possessing the characteristics of bleaching and disinfection.
Synthesis Methods of Hydrogen Peroxide
Direct Synthesis from Hydrogen and Oxygen
Theoretically, hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) can directly react to form hydrogen peroxide. However, in practical operation, this method is difficult to control and is prone to causing explosions. Therefore, this method is rarely used in industrial production.
Reaction equation:
2H₂ + O₂ ===catalyst 2H₂O₂
Anthraquinone Method (Industrial Synthesis Method)
The anthraquinone method is the main method for producing hydrogen peroxide in the industry at present. This method uses organic compounds (such as anthraquinone) as carriers and generates hydrogen peroxide through cyclic reactions of hydrogenation and oxidation. The basic reaction process is as follows:
Hydrogenation reaction:
C₁₅H₁₀O₂ + H₂ ===catalyst C₁₅H₁₂O₂
(Anthraquinone is hydrogenated to hydrogenated anthraquinone)
Oxidation reaction:
C₁₅H₁₂O₂ + O₂ ===catalyst C₁₅H₁₀O₂ + H₂O₂
(Hydrogenated anthraquinone is oxidized, and hydrogen peroxide is generated simultaneously)
Extraction and separation:
The generated hydrogen peroxide is separated from the reaction system through an extractant.
Electrolysis Method
The electrolysis method is to generate hydrogen peroxide by electrolyzing water, and this method is suitable for preparing a small amount of hydrogen peroxide in the laboratory.
Reaction equation:
2H₂O ===electrolysis H₂O₂ + H₂
Barium Peroxide Method
Barium peroxide (BaO₂) reacts with water to generate hydrogen peroxide, and this method is also suitable for preparing a small amount of hydrogen peroxide in the laboratory.
Reaction equation:
BaO₂ + H₂O = Ba(OH)₂ + H₂O₂
Sodium Peroxide Method
Sodium peroxide (Na₂O₂) reacts with water to also generate hydrogen peroxide, and this method is also suitable for preparing a small amount of hydrogen peroxide in the laboratory.
Reaction equation:
Na₂O₂ + 2H₂O = 2NaOH + H₂O₂
Conclusion
The anthraquinone method is the most commonly used synthesis method of hydrogen peroxide in the industry, which has the characteristics of high efficiency, safety, and large-scale production. The electrolysis method, barium peroxide method, and sodium peroxide method are more suitable for small-scale preparation in the laboratory.
China and chemical raw material suppliers, welcome to inquire,Contact us:https://www.yuhanchemi.com/contact