Is lead iodide soluble in water?
Solubility of Lead Iodide in Water: Facts and Truth
To answer the question directly: lead iodide (PbI2) is sparingly soluble in water, not completely insoluble. Although on a macroscopic level we often observe its formation as a distinct precipitate, this does not mean it doesn’t dissolve at all. In reality, a very small amount of lead iodide ions will dissolve in water, forming lead ions (Pb2+) and iodide ions (I−).

Solubility Data:

論點: Lead iodide is also known as Lead(II) iodide with the chemical formula PbI2.
邏輯類型: Identification
結論: Chemical Formula: PbI2
參考: https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/3741
參考:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lead(II)_iodide
参考:https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/24931
邏輯推理
結論: Lead iodide solubility at 25°C is 0.00158 gram-molecule per litre.
參考: http://lead.atomistry.com/lead_iodide.html
Yuhan lead iodide
产品:https://www.yuhanchemi.com/leadii-iodide
产品:https://www.yuhanchemi.com/products/phosgene-derivatives
New:https://www.yuhanchemi.com/news/industry-news
Under standard conditions (around 25°C), the solubility of lead iodide is very low, approximately 0.0013 g/100 mL or $\text{4.14 \times 10^{-5} mol/L}$. It’s important to note that the solubility of lead iodide increases slightly with increasing temperature. For example, at 50°C, its solubility is about 0.004 g/100 mL. These data clearly indicate that while the solubility is not high, it is not zero.
Solubility Equilibrium:
The dissolution of lead iodide in water is a dynamic equilibrium process. When solid lead iodide is added to water, a portion of it dissolves into ions, while the lead and iodide ions in the water also recombine to form solid lead iodide.:
PbI2(s)⇌Pb2+(aq)+2I−(aq)
Solubility Product Constant (Ksp):
To more precisely describe the solubility of sparingly soluble electrolytes, we introduce the concept of the solubility product constant (Ksp). For lead iodide, the Ksp expression is:
Ksp=[Pb2+][I−]2
The Ksp value for lead iodide is very small (approximately 7.1×10−9 at 25°C), which directly reflects its low solubility in water. The smaller the Ksp value, the lower the solubility of the substance in water. Through Ksp, we can calculate the equilibrium concentrations of iodide and lead ions in pure water, thus quantifying the solubility of lead iodide.

Factors Affecting the Solubility of Lead Iodide
Although lead iodide itself has low solubility in water, several external factors can influence its dissolution behavior:
Effect of Temperature:
As mentioned earlier, increasing the temperature generally increases the solubility of lead iodide. This is because heating provides additional energy for the dissolution process, helping to overcome the lattice energy and allowing more lead iodide ions to enter the solution. While the increase in solubility is not dramatic, it is still a factor to consider in certain applications.
Common Ion Effect:
adding potassium iodide increases the concentration of iodide ions in the solution. According to the solubility product equilibrium, to maintain the Ksp value, the concentration of lead ions must decrease, leading to the precipitation of more lead iodide:
PbI2(s)⇌Pb2+(aq)+2I−(aq)
Adding I− shifts the equilibrium to the left.
Effect of pH:
Since the iodide ion (I−) is the conjugate base of a strong acid (hydroiodic acid, HI), it is a very weak base. Therefore, changes in pH generally have little effect on the solubility of lead iodide. Only under very strong acidic conditions might some side reactions involving iodide ions occur, indirectly affecting the solubility equilibrium of lead iodide.
Other Factors:
Under normal experimental conditions, changes in pressure have a negligible effect on the solubility of solids in liquids, so the effect of pressure on the solubility of lead iodide in water can be ignored. Additionally, certain complexing agents might form stable complexes with lead ions, thereby increasing the solubility of lead iodide, but this usually occurs under specific chemical environments.
Preparation and Applications of Lead Iodide
Understanding the solubility of lead iodide is crucial for its preparation and applications.
Laboratory Preparation Methods:
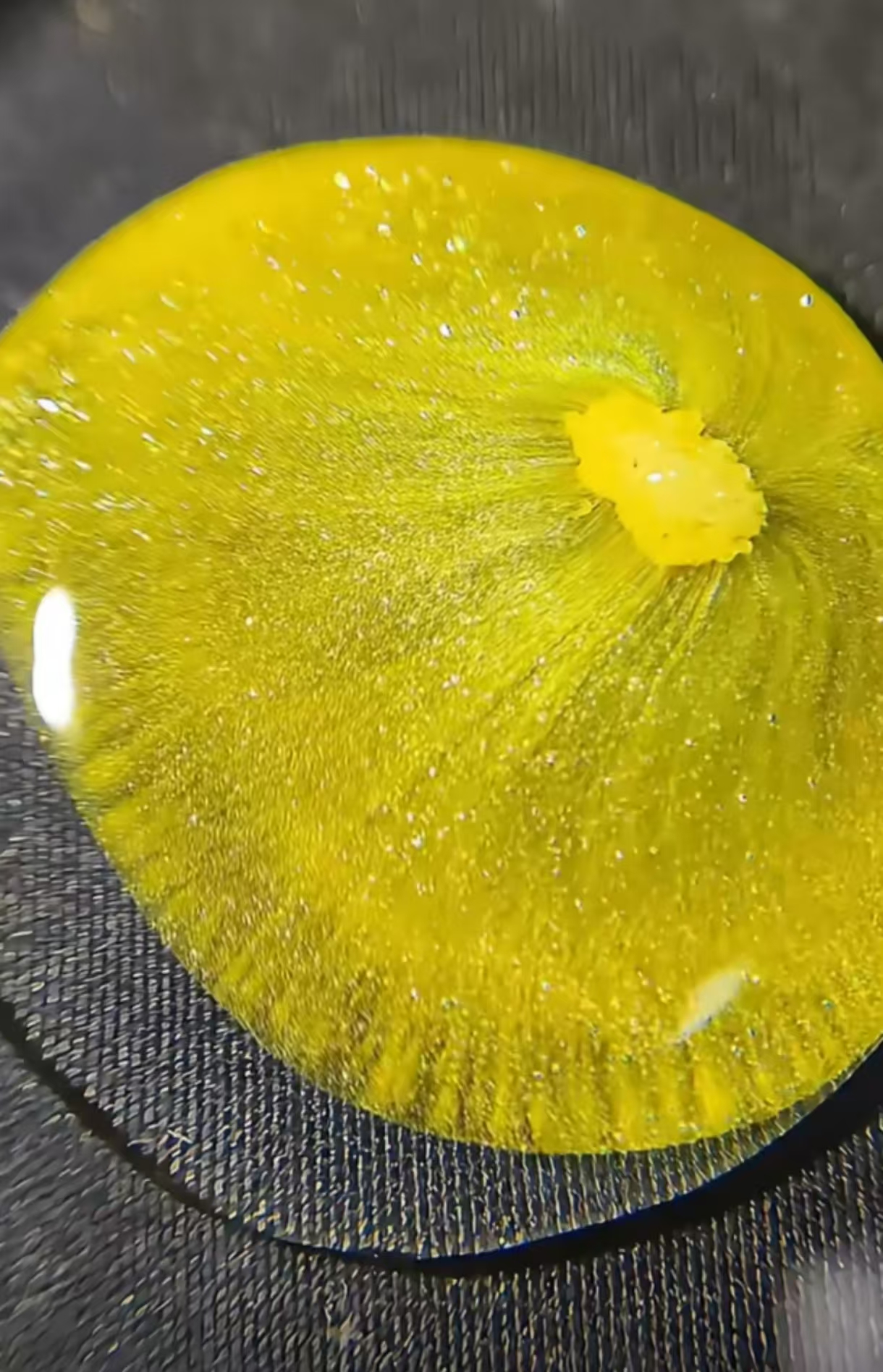
The reaction quickly produces an insoluble lead iodide precipitate, exhibiting a characteristic vibrant yellow color:
Pb(NO3)2(aq)+2KI(aq)→PbI2(s)↓+2KNO3(aq)
Pure lead iodide solid can be obtained through filtration, washing, and drying.
Main Application Areas:
Despite the toxicity of lead, lead iodide is still used in some areas due to its unique physicochemical properties:
- Pigment: Historically, lead iodide was used as a yellow pigment due to its bright color.
- Photovoltaic Material: In recent years, lead iodide has shown great potential in the research of perovskite solar cells. Perovskite-structured photovoltaic materials offer advantages such as low cost and high efficiency, and lead iodide is an important precursor for constructing these materials.
- X-ray and Gamma-ray Detectors: Lead iodide has a high atomic number and density, allowing it to effectively absorb X-rays and gamma rays. Therefore.
- Photography (Historical Application): In early photographic processes, lead iodide was used in the preparation of certain photosensitive materials.
- Other Potential Applications: Researchers are also exploring the potential applications of lead iodide in catalysis, sensing, and other fields.
Conclusion
In summary, lead iodide is sparingly soluble in water, not completely insoluble. Although the solubility is low, its dissolution equilibrium and solubility product constant are key to understanding its chemical behavior. From laboratory preparation to potential applications in emerging fields like photovoltaic technology, a thorough understanding of the solubility of lead iodide helps us better utilize this interesting compound.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the color of lead iodide precipitate? Lead iodide precipitate typically has a bright golden-yellow color.
- How can the solubility of lead iodide in water be increased? Increasing the temperature can slightly increase its solubility. Avoiding the addition of substances containing common ions can prevent further reduction in solubility.
- How significant is the common ion effect on the solubility of lead iodide? The common ion effect significantly reduces the solubility of lead iodide. Adding soluble salts containing Pb2+ or I− will cause more precipitate to form.
- Is lead iodide toxic? Yes, lead compounds are generally toxic. Appropriate safety precautions should be taken when handling lead iodide, and the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) should be consulted for detailed safety information.
We hope this article has clearly answered your question about “Is lead iodide soluble in water?” and helped you gain a deeper understanding of this important chemical substance.