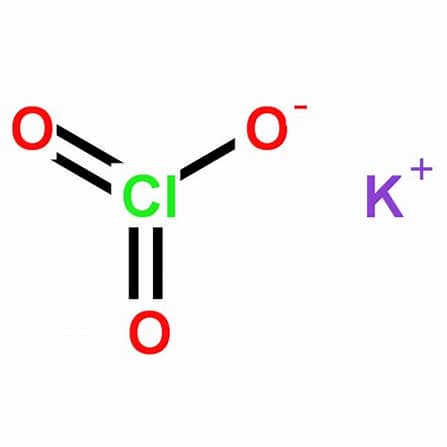
Potassium Chlorate (KClO₃)381-04-9.
I. Basic Information
Potassium chlorate (Potassium Chlorate), with the chemical formula KClO₃, is a colorless or white crystalline powder, salty and cool in taste, and belongs to a strong oxidant. This substance is stable at room temperature, decomposes and releases oxygen above 400°C. When mixed with reducing agents, organic substances, and flammable substances (such as sulfur, phosphorus, or metal powders, etc.), it can form an explosive mixture, and will explode when heated rapidly. Potassium chlorate is a highly sensitive explosive agent. When mixed with certain impurities, it may even explode spontaneously under sunlight, and will explode when it comes into contact with concentrated sulfuric acid. It is composed of ions. It is listed in the “List of Explosive Hazardous Chemicals” and is regulated in accordance with the “Administrative Measures for the Public Security Management of Explosive Hazardous Chemicals”.
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Chinese Name | Potassium Chlorate |
| English Name | Potassium Chlorate |
| Chemical Formula | KClO₃ |
| Molecular Weight | 122.549 |
| CAS Registry Number | 3811-04-9 |
| EINECS Registry Number | 223-289-7 |
| Melting Point | 356°C |
| Boiling Point | 400°C |
| Water Solubility | 73 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Density | 2.32 g/cm³ |
| Appearance | Colorless or white crystalline powder |
| Safety Description | S13; S16; S27; S61 |
| Hazard Symbol | Xn; O; N |
| Hazard Description | R9; R20/22; R51/53 |
| UN Dangerous Goods Number | 1485 |
II. Physical and Chemical Properties
(I) Physical Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 2.32g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 356°C |
| Boiling Point | 400°C |
| Appearance | Colorless or white crystalline powder |
(II) Chemical Properties
Potassium chlorate is a strong oxidant. In the presence of a catalyst, it can decompose at a relatively low temperature and release oxygen strongly. It has strong oxidizing properties in acidic solutions. When mixed with carbon, phosphorus, organic substances or combustible substances, it is likely to burn and explode when impacted. The relevant reactions of thermal decomposition are as follows:
The chemical equation for the reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid:
KClO₃ + H₂SO₄ = KHSO₄ + HClO₃
3HClO₃ = HClO₄ + 2ClO₂↑ + H₂O (Chloric acid is unstable and will disproportionate into perchloric acid, chlorine dioxide and water)
2ClO₂ = Cl₂ + 2O₂ (Chlorine dioxide is also unstable and will decompose into chlorine and oxygen)
Total reaction equation: 3KClO₃ + 3H₂SO₄ = 3KHSO₄ + HClO₄ + Cl₂↑ + 2O₂↑ + H₂O
The concentrations of chloric acid, perchloric acid and chlorine dioxide generated in this reaction are very high, and it is extremely explosive.
III. Computational Chemical Data
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Reference Value of Hydrophobic Parameter Calculation (XlogP) | None |
| Number of Hydrogen Bond Donors | 0 |
| Number of Hydrogen Bond Acceptors | 3 |
| Number of Rotatable Chemical Bonds | 0 |
| Number of Tautomers | 0 |
| Topological Molecular Polar Surface Area (TPSA) | 57.2 |
| Number of Heavy Atoms | 5 |
| Surface Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 49.8 |
| Number of Isotope Atoms | 0 |
| Number of Determined Atomic Stereocenters | 0 |
| Number of Undetermined Atomic Stereocenters | 0 |
| Number of Determined Bond Stereocenters | 0 |
| Number of Undetermined Bond Stereocenters | 0 |
| Number of Covalent Bond Units | 2 |
IV. Applications
Potassium chlorate has a wide range of uses. It can be used in explosives, fireworks, firecrackers, high-grade safety matches, etc. It also has certain applications in the medical field and can be used as a photographic reagent, analytical reagent, oxidant, as well as a propellant for rockets and missiles. Among the propellants of the same series, the propellant containing potassium chlorate burns faster than the propellant containing ammonium chlorate. The minimum pressure at which combustion can occur is relatively high, and the burning rate index is very high. In addition, it can also be used as a medicinal agent for relieving fever and promoting diuresis. However, in chemical laboratories, the method of heating potassium chlorate to prepare oxygen is not commonly used because the prepared oxygen is impure and dangerous.
V. Emergency Treatment
(I) Leakage Emergency Treatment
Isolate the leakage contaminated area and restrict access. It is recommended that emergency treatment personnel wear self-contained breathing apparatus and general work clothes. Do not directly contact the leaked substance, and avoid the leaked substance from contacting organic substances, reducing agents, and flammable substances.
- Small amount of leakage: Collect it in a dry, clean and covered container with a clean shovel.
- Large amount of leakage: Cover it with plastic sheeting and canvas to reduce dispersion. Then collect, recycle or transport it to a waste treatment site for disposal.
(II) Protection Measures
- Respiratory system protection: When there is a possibility of contact with its dust, it is recommended to wear a self-priming filter dust mask.
- Eye protection: Wear chemical safety goggles.
- Body protection: Wear polyethylene anti-virus clothing.
- Others: Smoking, eating and drinking are prohibited at the work site. Take a shower and change clothes after work, and maintain good hygiene habits.
(III) First Aid Measures
- Skin contact: Remove the contaminated clothing and rinse with plenty of water.
- Eye contact: Lift the eyelids, rinse with flowing water or normal saline, and seek medical attention in a timely manner.
- Inhalation: Quickly leave the site to an area with fresh air. Keep the respiratory tract unobstructed. If breathing is difficult, give oxygen. If breathing stops, perform artificial respiration immediately and then seek medical attention.
- Ingestion: Drink plenty of warm water and induce vomiting, and then seek medical attention.
VI. Storage Method
Store it in a sealed and cool place. Do not expose it to sunlight for a long time, and prevent it from contacting organic substances and other easily oxidizable substances. In particular, potassium chlorate should not be mixed with ammonium salts, otherwise ammonium chlorate will be formed, and ammonium chlorate may self-ignite or even explode spontaneously.
VII. Safety Information
(I) Safety Terms
- S13: Keep away from food, drink and animal feeding stuffs.
- S16: Keep away from sources of ignition – No smoking.
- S27: Take off immediately all contaminated clothing.
- S61: Avoid release to the environment. Refer to special instructions/Safety data sheets.
(II) Risk Terms
- R9: Explosive when mixed with combustible material.
- R20/22: Harmful by inhalation and if swallowed.
- R51/53: Toxic to aquatic organisms, may cause long-term adverse effects in the aquatic environment.