Product Details:
| parameter | United States | minimum | utmost | |
| Assay (H2O2) | % | 30.0 | 32.0 | |
| color | APA | 5 | ||
| Nitrate (NO3) | ppb | 50 | ||
| Total organic carbon (TOC) | ppm | 20 | ||
| Chloride (Cl) | ppb | 30 | ||
| Sulfate (SO4) | ppb | 50 | ||
| Phosphate (PO4) | ppb | 20 | ||
| Impurity maximum | United States | minimum | utmost | |
| Aluminum (Al) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Antimony (Sb) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Arsenic (As) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Barium (Ba) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Beryllium (Be) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Bismuth (Bismuth) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Boron (B) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Cadmium (Cd) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Calcium (Ca) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Chromium (Cr) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Cobalt (Co) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Copper (Cu) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Gallium (Ga) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Germanium (Ge) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Gold (AU) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Iron (iron) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Lead (Pb) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Lithium (Li) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Magnesium (Mg) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Manganese (Mn) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Molybdenum (Mo) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Nickel (Ni) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Niobium (Nb) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Potassium (K) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Silver (Ag) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Sodium (Na) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Strontium (Sr) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Tantalum (Ta) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Thallium (Tl) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Tin (Sn) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Titanium (Ti) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Vanadium (V) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Zinc (Zn) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Zirconium (Zr) | ppb | 0.05 | ||
| Particle count | United States | minimum | utmost | |
| ≧ 0.1 microns | pcs/ml | 300 | ||
| ≧ 0.2 microns | pcs/ml | 200 | ||
| ≧ 0.5 microns | pcs/ml | 100 | ||
| ≧ 1.0 microns | pcs/ml | 25 | ||
Physical and chemical properties
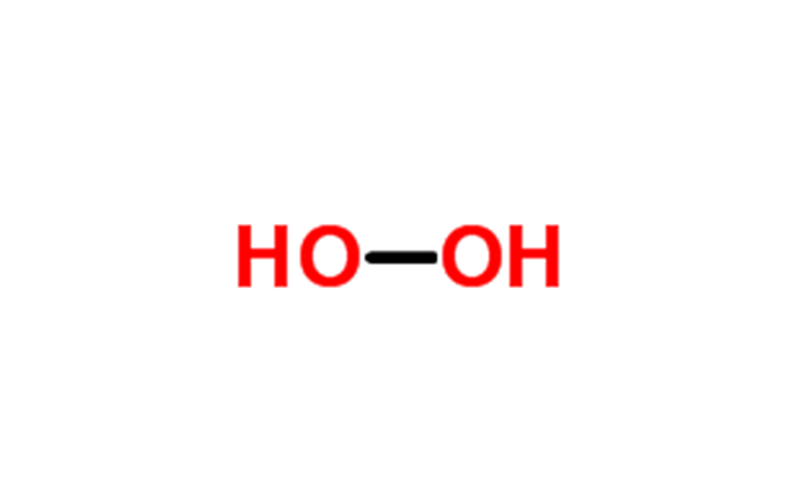
- Chemical Name: Hydrogen Peroxide
Hazardous Chemical Category: Class 5.1 Oxidizing agent, corrosive and highly irritating.
Physical and chemical properties of
hydrogen peroxide Appearance and properties: colorless transparent liquid, slightly irritating.
Melting/freezing point: -33°C (-0.43°C) Boiling
point: 108°C (150.2°C)
Density: 1.11g/cm3(20°C, 30% hydrogen peroxide)
PH value: 1-4
Solubility: soluble in water, ethanol, ether, insoluble in benzene
Stability: stable under normal conditions;
Flammability: Combustion
prohibited ingredients: metals and metal oxides; Alkali; Reducer; dust (accelerates its own exothermic decomposition reaction); combustibles, organic matter (explosive hazard), acetone (forms explosive mixtures);
Hazardous reactions: heat, or decomposition reactions with alkalis, reducing agents, and organic matter;
Hazardous decomposition products: water and oxygen;
Key Applications
- Semiconductor industry:
- It is used for wafer cleaning, etching, and removal of organic contaminants from microelectronics
- It is essential for the oxidation process and cleaning before lithography
- Electronics Manufacturing:
- High-purity etchants for circuit boards
- Used in the Chemical-Mechanical Planarization (CMP) process
- Chemosynthesis:
- Oxidizing agents in high-purity chemical production
- Used in the synthesis of fine chemicals and pharmaceuticals
- Environmental Applications:
- Wastewater treatment and air purification (advanced oxidation process)
- Used in disinfection and sterilization processes
- Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology:
- It is used for sterilization, sterilization, and as a precursor for drug synthesis
Stability of hydrogen peroxide
Instability is an important property of hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide decomposes spontaneously to produce water and oxygen:
2 H2O2 → 2H2O+ O2↑+ 46.94 kcal
The main factors affecting the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide are: temperature, light, pH, metal ions, etc.:
1. Temperature
H2O2Stable at low temperatures, high purity and normal conditions. Pure H2O2When heated to 153°C or higher, violent explosive decomposition occurs. At lower temperatures, the decomposition reaction is smooth and slow.
2. Lighting
Light with a wavelength of 3200-3800 Å can make H2O2Decomposition is faster.
3. Acidity and alkalinity
The pH of the medium is H2O2The stability of the game has a great impact. H under acidic conditions2O2stable in nature and slow decomposition; It is very unstable in alkaline media and decomposes quickly. In an alkaline solution, H2O2It has strong oxidizing properties. Therefore, heating an alkaline solution completely destroys excess H2O2 。
4. Metal ions
Many metal ions can be used as catalysts for hydrogen peroxide decomposition reactions, which affect H2O2An important factor in stability. For example, Fe2+、Mn2+、Cu2+、Cr3+ and so on can accelerate H2O2Decompose. Industrial grade H2O2Because it contains more metal ion impurities, a large number of stabilizers must be added to inhibit the catalytic effect of impurities through reduction and complexation.
Hydrogen peroxide safety
flammability
H at any concentration2O2Both are non-flammable, but it is a strong oxidizing agent that helps flammability, when H2O2When the concentration is high, it is easy to cause the combustion of other combustible substances. H2O2The process that causes combustion is the combination of its decomposition and oxidation. H2O2The higher the concentration, the easier it is to start combustion. When the spillover H2O2When in contact with combustible substances, rinse immediately with plenty of water.
Operability
H2O2In the presence of catalytic impurities, it can decompose, release oxygen and heat, temperature and H2O2The higher the concentration, the faster it decomposes. Therefore, once the reaction is induced, the decomposition accelerates itself with exothermic release, further increasing the temperature of the material and producing more gases (oxygen and vapor), which expands with the increase of temperature. Therefore, store H2O2The equipment should have dust-proof vents to safely release any gases that may be generated.
toxicity
H2O2In a general sense, it is non-toxic, when H2O2When it gets on the human body or splashes into the eyes, it has an irritating effect on the skin, eyes and mucous membranes. when the concentration is low, there is bleaching effect and burning sensation; When the concentration is high, it can cause the epidermis to blister and cause serious damage to the eyes; Steam inhalation into the lungs has an irritating effect, and in severe cases, it can lead to organ damage.
Safety and handling
- Hazard: Strong oxidizing agent, which can cause severe burns and eye damage. reacts sharply with organic substances and reducing agents.
- Storage:
- Store in sealed, compatible containers (e.g., HDPE, PFA).
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated place away from sunlight and heat
- Protective Equipment: Wear chemically resistant gloves, goggles, and lab coats. Use in a well-ventilated space or under a fume hood.